Employers? Hire Better With Our Aptitude Test
A short guide of basic and advanced formulas that will boost your performance on your upcoming numerical reasoning test.
Introduction
In order to succeed on the Numerical Reasoning Test you are scheduled for, no matter it's type, you will need to have first mastered some basic maths skills.
Numerical aptitude tests usually target the following mathematic skills: 1) Addition 2) Subtraction 3) Multiplication 4) Division 5) Averages 6) Percentages 7) Ratios.
More advanced calculations, such as averages, percentages and ratios can become simpler with the use of specific formulas.
Such is the case with algebraic questions that involve rate problems (work/ speed/ distance/ time) as well as financial-oriented problems.
For your benefit, we assembled here a short guide to basic as well as advanced formulas that you are expected to be able to apply in your numerical test.
Let's Get Started!
Ace Your Job Search with a Custom Prep Kit
Job hunting doesn't have to be stressful.
Prepare smarter and ace your interviews faster with our Premium Membership.



Averages
Definition: A calculated “central” value of a set of numbers.
The formula to calculate this looks like this:

in a more mathematical form it would look like this:

Where:
Xi = An item in the set; X1, X2, X3 ...
∑ = Sum
N = The number of items in the set
X̅ = The average of set X
Weighted average
Definition: A calculated “central” value of a set of numbers, in which each value or set of values is assigned a different weight.
The formula to calculate this looks like this:
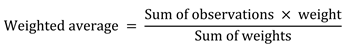
and in mathematical form:

Where:
Xi = An item in the set; X1, X2, X3 ...
wi = The weight of item i in the set
∑ = Sum
N = The amount of the items in the set
X̅ = The weighted average of set X
In a simplified form, it can be put as:
For example: the heights of students in a classroom were measured. There are 2 children at 1.20 m, 3 children at 1.25 m and 3 children at 1:30 m.
What is the average height of a student in the classroom?
Solution:
Percentages & Fractions
Definition: A percentage is a part of a whole, where the whole is defined as 100. A fraction is a part of a whole, where the whole can be any number.
The formula to calculate this looks like this:
% = (fraction) x 100
Note that when dealing with percentages it is sometimes easier to convert them into decimals and use the decimals in percentages calculations.
For example: 50% = 0.5; 120% = 1.2; 11% = 0.11 etc.
Calculating a percentage
The formula:
% = (Value/Total) x 100
For example: if you own 20 company shares and the total number of shares is 400, this means you own: 20/400= 5% of the shares.
Percentage Increase/Decrease
The formulas:
% Increase:
New value = (1+ Increase) × (Original amount)
% Decrease:
New value = (1 − Decrease) × (Original amount)
For example: if a shirt cost £30 and a week later was offered at a 15% discount, how much does the shirt cost? 91 − 0.15) × 30 = 0.85 × 30 = £25.5
Calculating Percentage Change
Definition: Percentage change refers to the relative percent change of an increase or decrease in the original amount.
% Increase:

% Decrease:

For example: if a shirt cost £30 and a week later was offered for the price of £24, what was the discount on that shirt? (30-24/30) x 100 = 20%
Note: Percentage change is different from absolute change. While percentage change is calculated in relation to the original amount, absolute change is calculated as an absolute amount.
In other words, it is not divided by the original amount.
Calculating Percentage Difference
Definition: Percentage difference refers to the relative percentage change in a certain amount, when you are not able to determine which amount is the original one.
For example: “Molly's designs” gets 200 customers a week while “Best wear” gets 240 customers. What is the percentage difference in customers between the two stores?
Reversed Percentages:
% Increase:
% Decrease:
For example: if a shirt costs £33 after a 20% increase in price, how much did it cost prior to the price change?
Percentage Points
Definition: Percentage points refer to an increase or decrease of a percentage. This is an absolute term (in contrast to percentage change/difference).
The formula looks like this:
Percentage points difference = New percent − Old percent
Now use what you learned in practice in your free numerical percentages test
Ratios
Definition: The relative size of two or more values. The values are usually separated by a colon sign.
a:b is a given ratio. N is the total sum of items.
The number of a items =

For example: there are 70 red and blue marbles in a jar. The ratio of red to blue marbles is 3:4. How many red marbles are there?
Now use it to solve your free numerical ratios test
Rate Formulas
What are rate problems?
A rate is a mathematical way of relating two quantities, which are usually measured in different units.
Rate problems usually involve three variables such as speed/distance/time or product/time/number of workers etc.
You are usually given 2 variables and are required to find the missing variable according to the data given in the question.
Speed: S = V × T
S = distance
V= velocity
T = time
Work: W = P × T
W = work
P = power
T = time
For example: Jill drove across a 0.3 mile long bridge. The time it took her car to travel from one side to the other was 20 seconds. How fast was Jill driving?
0.3 = V x 20 ⇾ 0.3/20 ⇾ V = 0.015 Miles per second (or 0.9 miles per minute).
Finance
Fixed and variable costs:
Fixed costs are set expenses a company has which never change and variable costs are costs that vary depending on a company's production volume.
Total cost = Fixed costs + Variable costs
For example: if the rent a pencil company pays for its offices is £100 per month, each pencil costs them £0.10 to make, and they make 100 pencils each month.
What is the company's total monthly cost?
Total cost = 100 + (0.10 x 100) = 100 + 10 = £100
Return on Investment (ROI):
Measures the profitability of an investment expressed as a percentage.

Profit margin:
Measures how much out of every dollar of sales a company actually keeps in earnings.

Good luck!
More Free Practice
We at JobTestPrep find the assessment tests world highly diverse and fascinating. If you are looking to deepen your knowledge in the aptitude tests world, or you want some extra practice before your test, we've got you covered!
Check out these fantastic free practice tests (all are completely free):
Free Aptitude Test | Free Psychometric Test | Free Numerical Reasoning Test | Free Verbal Reasoning Test | Free Cognitive Test | Free Critical Thinking Test | Free Abstract Reasoning Test | Free Spatial Reasoning Tets | Free Personality Test | Free Inductive Test | Free Mechanical Reasoning Test



